Description
The nutritive value of feeds for ruminants has been accessed by mathematical modeling related to the dynamics of digestion and passage in the rumen. Previous modeling developments (Ellis et al., 1994; France et al., 1998; Mertens 1993) have been parameterized to be used in the interpretation of in situ and in vitro kinetic studies with the main objective of estimating parameters related to the microbial digestion of the feed retained in the rumen.
Mechanistic models derived through compartmental analysis yield deterministic solutions that can be used for practical applications as well as theoretical development. Models designed to describe degradation profiles have been evaluated for quality of fit and validity of assumptions (Van Milgen and Baumont, 1995; Ellis et al., 2005). These particular models were designed in accordance to a general scheme in which the ingested feed is forced to exit the rumen but some is digested while retained in the rumen. The degree of complexity whereby digestion and passage phenomena are integrated varies among different approaches.
Most mathematical models that simulate the dynamics of fiber degradation and passage assume the digesta fiber is part of a single pool. The ruminal fiber pool is heterogeneous for ruminants consuming enough fiber that promotes the natural stratification of the digesta. The GnG1 model is an alternative model that was developed and evaluated to accommodate the digesta stratification. The GnG1 model can be used either under steady-state or dynamic conditions by treating the fiber mass in the rumen as a sequential of two pools of fibrous particles (Vieira et al., 2007a,b,c).
The GnG1 model was developed based on theoretical concepts and probability to generalize the rumen processes of fiber digestion. It can be used to interpret fiber degradation and passage profiles. The GnG1 model was evaluated for quality of fit using in vitro fiber degradation profiles and in vivo fiber passage profiles. The integration of digestion and passage is based on the concept that fibrous digesta in the rumen is heterogeneous (Vieira et al., 2007a,b,c).
|
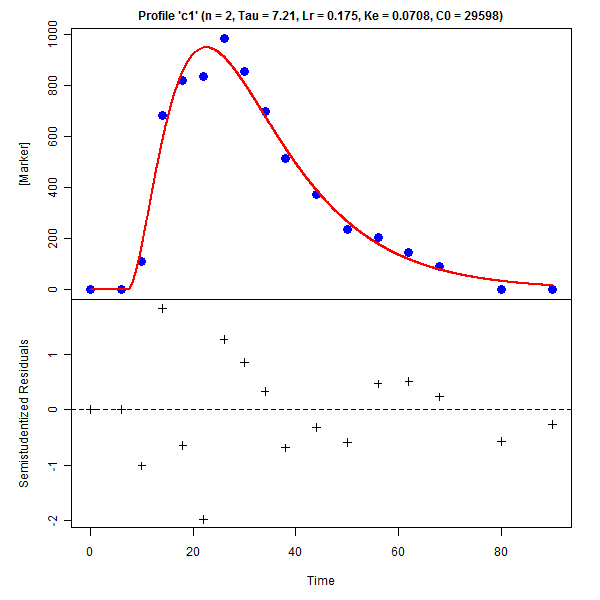
GnG1 Model fitting for degradation profile |
|
|
Download
|
It uses R! |
Visual Studio 2022 |
|
32 bit and 64 bit Compatible |
|
The GnG1 Models software is programmed with the Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 using Visual Basic and .NET 4.0 framework (click here to download .NET 4.0 framework). It uses R scripting v. 2.0 or later technology (Click here to download R) to perform calculations, nonlinear convergence, and high-quality graphic production. It works with most IBM-PC compatible computers that have Microsoft Windows 7 or later. In order to execute GnG1 Models, you have to install the following packages: XML and chron. Even though GnG1 Models will try to install them automatically, you may install them manually. Briefly, after you have installed R, open R, click on menu packages, and then install packages. Select the provider and then select the package one at a time. You have to have internet connection active to download the packages. There is a Visual Basic Script (Install R Packages.VBS) in the GnG1 Models folder that performs the installation of these packages automatically. |
|||
The current version of the GnG1 Models is Loading...
What is new in GnG1 Models versions later than 2.0 ? NEW
- 1. New interface (degradation and passage) facilitates user communication.
- 2. Allows user to stop calculations, and
- 3. Completely integrated and re-designed R scripts.
Previous versions can be downloaded from here.
- The latest script for GnG1 is:
- GnG1 script 2.4.11
- Unzip the zip file and copy the .ZZZ files to the My Documents\TAMU\GnG1\Scripts folder
A tutorial on how to install the GnG1 Models is available at the Media web page. web page.
Registration
The GnG1 Models will expires after 5 trial uses if it is not registered by the end of the grace period. You may register your copy by submitting the license number on the Register webpage. If applicable, registration codes are issued only after the full registration fee has been paid on the Purchase webpage.
Developers
Support
The following list summarizes corrections, enhancements, and functional improvements made to the software, presented in chronological order (newest to oldest). Each entry reflects updates implemented to improve stability, usability, and overall performance.
There are no corrections, enhancements, or functional improvements to report at this time. However, several related documents, manuscripts, and reports are listed on the Publications web page, such as:
- Vieira, R. A. M., L. O. Tedeschi, and A. Cannas. 2007a. A generalized model for describing fiber dynamics in the ruminant gastrointestinal tract. 1. The heterogeneity of the pool of fiber particles in the ruminoreticulum. 2007 Beef Cattle Report in Texas. Texas A&M University, College Station, TX. 97-102 p.
- Vieira, R. A. M., L. O. Tedeschi, and A. Cannas. 2007b. A generalized model for describing fiber dynamics in the ruminant gastrointestinal tract. 2. Accounting for heterogeneous pools in the ruminoreticulum. 2007 Beef Cattle Report in Texas. Texas A&M University, College Station, TX. 103-110 p.
- Vieira, R. A. M., L. O. Tedeschi, and A. Cannas. 2007c. A generalized model for describing fiber dynamics in the ruminant gastrointestinal tract. 3. Estimating digestion-related kinetic parameters. 2007 Beef Cattle Report in Texas. Texas A&M University, College Station, TX. 111-120 p.
Links
This section will be updated with relevant links as they are identified and curated for this model.