Description
The Ruminant Nutrition System (RNS) is a mechanistic, biology-driven nutrition model developed to represent the underlying processes governing feed intake, digestion, rumen fermentation, nutrient supply, and animal responses in ruminants, as described in the Blue and Red RNS books. The primary objective of the RNS model is to perform the biological and physiological calculations associated with feeding ruminant animals, rather than relying solely on empirical prediction. At its core, RNS is a systems-based model that integrates knowledge of ruminal microbial activity, feed fractionation, nutrient flows, and animal metabolism to predict energy and protein supply and requirements across physiological states, species, and production systems. The model is designed to explicitly represent cause-and-effect relationships within the ruminant digestive system and to remain adaptable as scientific understanding evolves.
- Scientific Foundations and Model Components. The RNS model builds upon and extends published equations and model structures from foundational ruminant nutrition research. These components are integrated into a coherent
framework that ensures internal consistency between dietary inputs, ruminal processes, and animal-level outputs.
- Mechanistic descriptions of carbohydrate and protein fractionation
- Models of rumen fermentation, volatile fatty acid (VFA) production, and ruminal pH
- Passage rate submodels governing digesta kinetics
- Microbial growth and nutrient requirements, including branched-chain amino acids
- Nitrogen cycling within the animal
- Body reserve dynamics and their interaction with maintenance and production requirements
- Species-specific nutrient requirement models for cattle, sheep, and goats
- Levels of Model Solution. The RNS framework supports multiple levels of solution, allowing users to select the degree of biological detail appropriate for their application. This tiered structure allows RNS to be
used for both routine diet evaluation and advanced research applications.
- Level 0 – User-supplied values for total digestible nutrients (TDN) and ruminally degraded protein (RDP)
- Levels 1 and 2 – Static, mechanistic prediction of energy and protein supply based on published CNCPS-derived structures
- Level 3 – Dynamic prediction of ruminal fermentation, VFA production, and pH
- Level 4 – Stochastic modeling of key biological variables using R (future implementation)
- Computational Architecture and Extensibility. The RNS model is implemented in a flexible computational environment that supports different calculation logic platforms. This architecture allows RNS to function not only
as a decision-support tool, but also as a research platform for developing and evaluating new nutrition concepts.
- Execution of custom R scripts for advanced calculations, graphics, reporting, and simulation
- Integration with dynamic modeling platforms (e.g., ExtendSim®) for continuous-time simulations
- Rapid prototyping and testing of new equations, submodels, and biological hypotheses
- Modeling Philosophy and Future Direction. The RNS model was developed with the explicit recognition that nutrition modeling must evolve alongside advances in biology, genomics, and computational science. While data-driven methods such as machine learning are increasingly available, RNS emphasizes that mechanistic understanding remains essential for interpreting biological responses and extrapolating beyond observed data.
Accordingly, RNS is structured to support future integration with hybrid knowledge- and data-driven approaches, ensuring that emerging computational techniques complement—rather than replace—biological realism.
The RNS software uses published equations and model structures as listed below:
- Equations published for the Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System (CNCPS) for cattle and sheep by Fox et al. (2004), Tylutki et al. (2008), Tedeschi et al. (2008), and Cannas et al. (2004, 2005; 2007);
- Nutrient requirements of goats (Cannas et al., 2007; Tedeschi et al., 2010);
- The body reserves model developed by Tedeschi et al. (2006);
- Nitrogen cycling model developed by Lanzas (2006);
- Feed carbohydrate and protein fractionation systems developed by Lanzas et al. (2007);
- A revised rumen submodel that includes:
- A volatile fatty acids (VFA) submodel adapted from Pitt et al. (1996);
- Ruminal passage rate submodels developed by Seo et al. (2006); and
- Prediction of microbial requirements for branched-chained amino acids as described by Tedeschi et al. (2000).
- Model structures that include:
- RNS for R, which has an extra capability to execute R scripts that quickly add customized calculations, high-quality graphics, reports, and advanced simulations such as stochastic modeling;
- Added capability to communicate with ExtendSim® in order to perform dynamic, continuous calculations; and
- Four levels of solution for predicting supply of energy and protein, as follows:
- 0 - User-inputted values for total digestible nutrients (TDN) and ruminally-degraded protein (RDP) for each dietary ingredient;
- 1 - Level 1 supply as described in Fox et al. (2004) with some modifications described in Tylutki et al. (2008);
- 2 - Level 2 as described in Fox et al. (2004) with some modifications described in Tylutki et al. (2008);
- 3 - Dynamic prediction of rumen VFA production and pH; and
- 4 - Stochastic modeling of key variables using R
- Future additions will include:
- Energy spilling and obligated amino acid fermenting bacteria pool (J. B. Russell, personal communication)
The RNS is being designed to meet the needs for the following applications: (1) teaching, (2) research, and (3) decision support system for use by field-oriented, consulting nutritionists.
Click here to start a tutorial on how to use the Ruminant Nutrition System.
Download
|
|
|
32 bit and 64 bit Compatible |
|
|
A computer with the following configuration is suggested for satisfactory performance: 2 GHz Intel Core Due (or similar) with at least 2 Gb of RAM. A CD/DVD-ROM for installation from CD media, an IBM-PC compatible printer, and an internet connection for updating and registration are recommended. The RNS requires 32-bit Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 to be installed in the computer. You may download the appropriate Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable setup (free of charge) that is compatible with your computer (click here to download Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable). See SUPPORT if this does not work. The RNS is programmed with the Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 using Visual Basic and .NET 4.7.1 framework. Users should download the .NET framework 4.7.1 using the web installer or the offline download. It uses R scripting v. 3.x technology or later (Click here to download R) to perform advanced simulations, customized calculations, and high-quality graphic production. Additional simulations can also be performed through ExtendSim® RunTime. In order to execute RNS for R the following R packages have to be previously installed: XML and Tcl/Tk. Even though RNS will try to install them automatically (need internet connection), you may install them manually by following these steps:
|
|||
The current version of the Ruminant Nutrition System is Loading...
 Please note that installation of this version may require a new registration if upgrading from older versions.
Please note that installation of this version may require a new registration if upgrading from older versions.
Previous versions of the RNS and recent versions of the RNS for R Scripts can be downloaded from here. The RNS for R Scripts have extensions .ZZZ or .ZZX.
Registration
The RNS will expire after 10 trial uses if it is not registered by the end of the grace period. You may register your copy by submitting the license number on the Register webpage. If applicable, registration codes are issued only after the full registration fee has been paid on the Purchase webpage.
Developers
Support
The following list summarizes corrections, enhancements, and functional improvements made to the software, presented in chronological order (newest to oldest). Each entry reflects updates implemented to improve stability, usability, and overall performance.
November 14, 2025. Third ERRATA for the first edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book (Volume II). Click here to download it.
June 6, 2024. Second ERRATA for the first edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book (Volume II). The variable rum.fd.bact.CHOB1.rate was previously assigned two different meanings: (1) the daily yield of bacteria from CHO B1, and (2) the bacterial composition of CHO B1. To resolve this issue, rum.fd.bact.CHOB1.rate is now solely assigned to represent the daily yield of bacteria from CHO B1. New variables were created for the bacterial composition of CHO B1. Click here to download it.
March 25, 2024. First ERRATA for the first edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book (Volume II). Click here to download it.
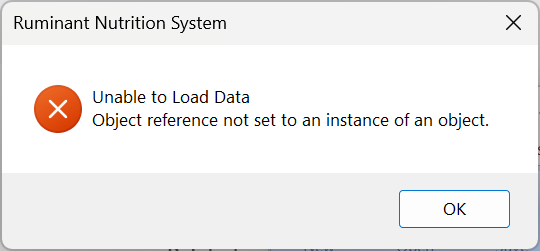
December 3, 2023. The 2007 and 2010 Microsoft Access Engines are required to access the feed library database and perform database manipulations. If you receive the warning message below, close the RNS and other programs to avoid loss of data, download this ZIP file, and install the three files in sequence: Setp 1, Step 2, and Step 3.
November 10, 2023. The Ruminant Nutrition System (RNS) requires .Net Framework 4.8.1. If your computer does not have it, you can install if from Microsoft .Net Framework site.
August 30, 2021. First ERRATA for the third edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book (volumes I and II). Click here to download it.
February 27, 2020. The 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' provider is not registered on the local machine error occurs, as shown below.
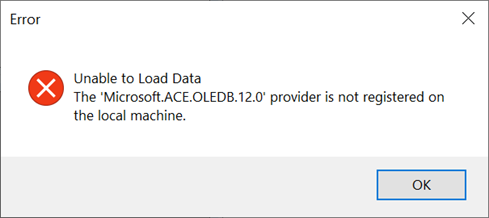
Download the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable from our website and install it with the option /quiet, using the CMD, as follows: C:\[DOWNLOAD FOLDER ]\AccessDatabaseEngine.exe /quiet. Alternatively, download it from Microsoft website.
June 24, 2018. First ERRATA for the second edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book. Click here to download it.
June 18, 2018. Adding a short path (a.k.a., short name) to a user name folder in Windows 10. As described on the November 11, 2017 note (below), users may receive an error when the user name folder does not have an equivalent DOS 8.3 short name. Users cannot simply add a short name to a user name folder because it is protected by Windows. Here is an workaround that works.
- Create a temporary administrator user account using the Control Panel and User Accounts
- Restart the computer, and login on this temporary user account
- Restart the computer on minimal safe boot mode, using MSCONFIG
- Start CMD as administrator, using Win+R
- Go to the root of the user name folder you want to add the short name, usually "C:\Users\", using "cd c:\users"
- Type "fsutil 8dot3name set 0" to enable the creation of short names
- Type "fsutil file setshortname 'USER NAME' USERNA~1" to create the short name to the folder "USER NAME"
- Type "dir /x" to show the folder and file names in the users root
- Restart the computer on normal boot mode, using MSCONFIG
- Login to the old "USER NAME" account, use the visual basic script shown in the November 11, 2017 note (below) to verify if the short name was set correctly
- Delete the temporary user account, using the Control Panel and Users Account
More information on the use of fsutil can be found at https://ss64.com/nt/fsutil.html.
November 11, 2017. When executing RNS for R, the following error occurs: "'fsutil' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file." This problem usually happens when there is no short path (DOS equivalent naming of 8.3) assigned to a folder, usually the username folder in Windows (C:\Users\UserName). This is a problem associated with Windows; the following links describe this problem.
- https://manjusullad.wordpress.com/2016/01/06/how-can-i-find-create-short-path-for-windows-folders-directories/
- https://ss64.com/nt/fsutil.html
- https://github.com/coreybutler/nvm-windows/issues/41
- https://superuser.com/questions/681330/how-to-force-short-name-8dot3-generation
- The following Visual Basic Script (.VBS) shows the short name of any file/folder
Set fso=CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
If fso.FolderExists(WScript.Arguments(0)) Then 'Folder
Set objFolder = fso.GetFolder(WScript.Arguments(0))
ok = InputBox("Short path:", "SHORT PATH", objFolder.ShortPath)
End If
If fso.FileExists(WScript.Arguments(0)) Then 'File
Set objFile = fso.GetFile(WScript.Arguments(0))
ok = InputBox("Short path:", "SHORT PATH", objFile.ShortPath)
End If
October 22, 2017. Second ERRATA for the first edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book. Click here to download it.
February 25, 2017. First ERRATA for the first edition of "The Ruminant Nutrition System" book. Click here to download it.
March 20, 2017. The CPU Usage crashes. This is a problem with the registry of the performance counters of your computer (more information here). The RNS provides two Visual Basic Scripts that might fix this problem. Execute the "FixPerfCtrl.VBS" located in the "C:\Program Files (x86)\TAMU\RNS". You must have administrative privileges to execute this VBS.
April 10, 2015. The 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' provider is not registered on the local machine error occurs, as shown below.
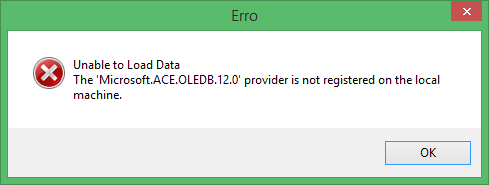
On 64-bit Windows and 64-bit Office (2010, 2013) environments, there are many reports on this error. The fix or workaround is a bit strange but seems to work for most people out there. If this error persists, even after installing
the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable, then instead try installing the 2007 Office System Driver: Data Connectivity Components
(
Source1, Source2).
UPDATED (April 2019). Apparently, the link to the 2007 Office System Driver: Data Connectivity Components is not working. Click here to download the zipped drives. Unzip the file, firstly install the "1-AccessDatabaseEngine_2007" file and secondly install the "2-accessruntimeanddataconnectivity2007sp3-kb2526310-fullfile-en-us" file, and then restart the computer.
INSTALL 32 bit version of Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable. Uninstall 64 bit version if previously installed. The RNS connection manager is trying to use the ACE OLE DB provider in order to access the Access file when the version is above 2007. Although your computer is 64-bit, you’re using SQL Server Data Tools, which is a 32-bit application. There is no 64-bit version for SSDT. When you design your package within SSDT, you’re using a 32-bit process, which can only use 32-bit providers. When you try to choose the table in the Access file, the connection manager needs to access the 32-bit version of the ACE OLE DB provider, but this provider is not registered on your machine, only the 64-bit version is installed. You should download the 32-bit version of the “Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable”. When you try to install it, you might get an error message. You should first uninstall only the 64-bit version of the “Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable”, which you probably installed previously. The 64-bit version and the 32-bit version can’t live together on the same host, so you’ll have to uninstall (through “Program and Features”) and install the other one if you wish to switch between them. Once you finish uninstalling the 64-bit version and installing the 32-bit version of the provider, the problem is solved, and you can finally choose the table within the RNS feed library file. The RNS connection manager is now able to use the ACE OLE DB provider (32-bit version) in order to access the Access file. (Source3)
Parameter Change. The form below is used to request a code to unlock the parameter values in the Ruminant Nutrition System settings page. After unlocking it, the user is able to change the parameter values. This code is provide under specific conditions only.
Links
- The latest books are available as hardcover, or paperback (and digital) editions from Kendall-Hunt (hardcover: Volume I and Volume II, or softcover: Volume I and Volume II), or Amazon.com (Volume I and Volume II).
- The CNCPS manual is a PDF file that contains the description of the model, tutorial, and the equations used to develop the model.
- The Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System web page.
- The Cornell-Penn-Miner (CPM) Dairy web page.
- The AMTS web page.